AWS CloudFormation introduction

This tutorial helps you to understand and script AWS CloudFormation.
AWS CloudFormation
CloudFormation Templates can be considered as Infrastructure as Code (Iac). Iac is a method of applying application development processes and best practices to the provisioning and deployment of infrastructure. CloudFormation is a service that helps us to model and set up our AWS resources.
Advantages:
- Ability to view/ manage/ delete all resources under a single stack using a single template file.
- Easy to recreate the same resources in a new account.
- Track and control changes to our Infrastructure.
Terminology:
1) CloudFormation Templates
Infrastructure as Code written in JSON OR YAML. The file will be the blueprint for building AWS resources. We can use this template to Create/Delete/Update aws resources
2) Stacks
Output of the template with all related resources described in the template as a single unit. Stack is the collection of AWS Resources.
3) Change Set
If we want to modify the existing template and update the stack. We can create a change set which allows us to see what are the changes to be executed in the existing stack.
Working of CloudFormation
Scenario 1 : Creating a Stack from a new template
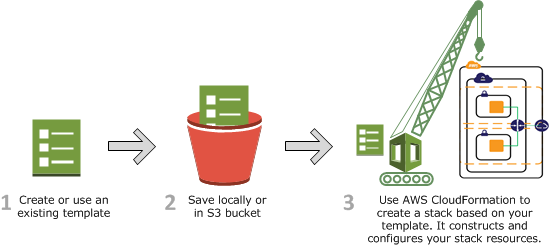
We can use any text editor or AWS CloudFormation Designer to write the cloud formation template. We prefer to use YAML over json because we can add comments in YAML.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09' # Mandatory
Description: A simple EC2 instance
Resources:
EC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
ImageId: ami-0ff8a91507f77f867
InstanceType: t2.micro
Scenario 2: Updating the stack.
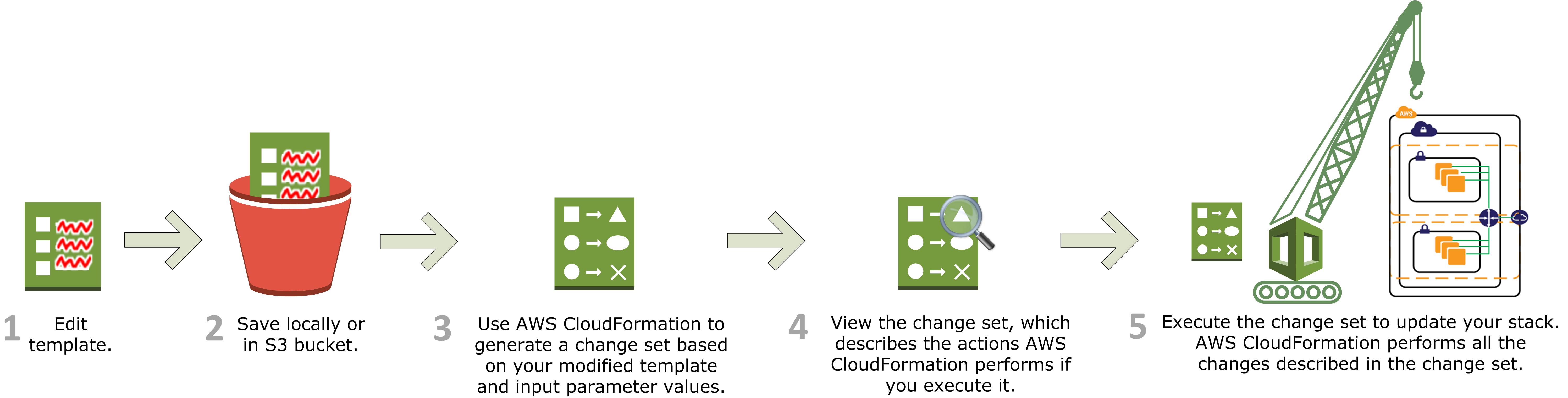
Modify the template file Save the file in local or s3 Execute the file to view and review the changesets to be made on the existing stack. Execute the change sets.
Scenario 3: Deleting a stack
We can delete the stack using console, CLI or API.
CloudFormation Template Structure:
- Format Version
- Description
- Metadata
- Parameters
- Rules
- Mapping
- Conditions
- Transformation
- Resources
- Output
Format Version:
Identifies the capabilities of the template (latest version is 2010-09-09).
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09' # Mandatory
Description:
Comments or Description of the template.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09' # Mandatory
Description: A simple EC2 instance
Metadata:
To provide specific description for the individual resources inside the template.
Metadata:
Databases:
Description: "Information about the databases"
Parameters:
Parameters allow us to inject custom values to our template each time while running the CloudFormation template.
Parameters:
EnvironmentParameter:
Type: String
Default: dev
AllowedValues:
- dev
- uat
- prod
Description: Environment Value
Rules:
We can create rules to add conditions or validation of parameters. Rules Consist of 2 properties Rule condition : when to take rule! Assertion: what value! .
Rules:
testInstanceType:
RuleCondition: !Equals
- !Ref Environment
- dev
Assertions:
- Assert:
'Fn::Contains':
- - a1.medium
- !Ref InstanceType
AssertDescription: 'For a dev env, the instance type a1.medium'
Mappings:
If we want to have a set of values based on some parameter value, we can use mapping. Eg If we want to have values based on the environment property we can use mapping. .
Parameters:
EnvironmentParameter:
Type: String
Default: dev
AllowedValues:
- dev
- uat
- prod
Description: Environment Value
Mappings:
EnvironmentMap
dev:
DomainName: dev.t2run.org
InstanceType: m1.small
sit:
DomainName: sit.t2run.org
InstanceType: a1.medium
prod:
DomainName: t2run.org
InstanceType: a1.large
Resources:
EC2Instance:
Type: "AWS::EC2::Instance"
Properties:
ImageId: ami-047bb4163c506cd98
InstanceType: !FindInMap [EnvironmentMap , !Ref EnvironmentParameter, InstanceType]
Conditions:
Statements which will define conditions under which the entities are created or configured. This condition will be used while creating the entities. The entities will be created only if the condition is true.
Conditions:
CreateProdResources: !Equals
- !Ref EnvironmentParameter
- prod
NewVolume:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::Volume'
Condition: CreateProdResources
Properties:
Size: 100
AvailabilityZone: !GetAtt
- EC2Instance
- AvailabilityZone
Here the AWS::EC2::Volume' will be created only if the condition CreateProdResources is true (only when the environment value is prod)
Transform:
We can define macro or use predefined macro to preprocess the the entire template before executing.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: 'AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31'
Resources:
AWS Resources which we are creating using the template under a stack.
Resources:
MyEC2Instance:
Type: "AWS::EC2::Instance"
Properties:
ImageId: "ami-047bb4163c506cd98"
Outputs:
Output values as result of executing the stacks. These values can be used to display information as logs or to import those values in other stacks.
Outputs:
Logical ID:
Description: Information about the value
Value: Value to return
Export:
Name: Name of resource to export
Summary:
We learned the basics of cloudformation. How it works, How to write, How to structure, Usage of different options and features.
